The YELLOW III Study (NCT04710368) demonstrated how 26 weeks of Evolocumab could reduce NIRS mxLCBI (-93.7) and IVUS PAV (-1.38%) in non culprit lesions in stable angina patients. View the study and watch Dr. Annapoorna Kini’s interview at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2023 Annual Scientific Sessions.
While heart attacks are usually caused by the narrowing or complete blockage of the coronary artery due to plaque buildup, plaque can also break loose, causing a clot blockage large enough to trigger a heart attack.
Different plaques have different composition, and not all plaques are prone to rupture. Fibrotic, or calcified, plaques, are more stable and less prone to rupture. Lipid Core Plaques (LCP), on the other hand, have thin fibrous caps, making them vulnerable to rupture.
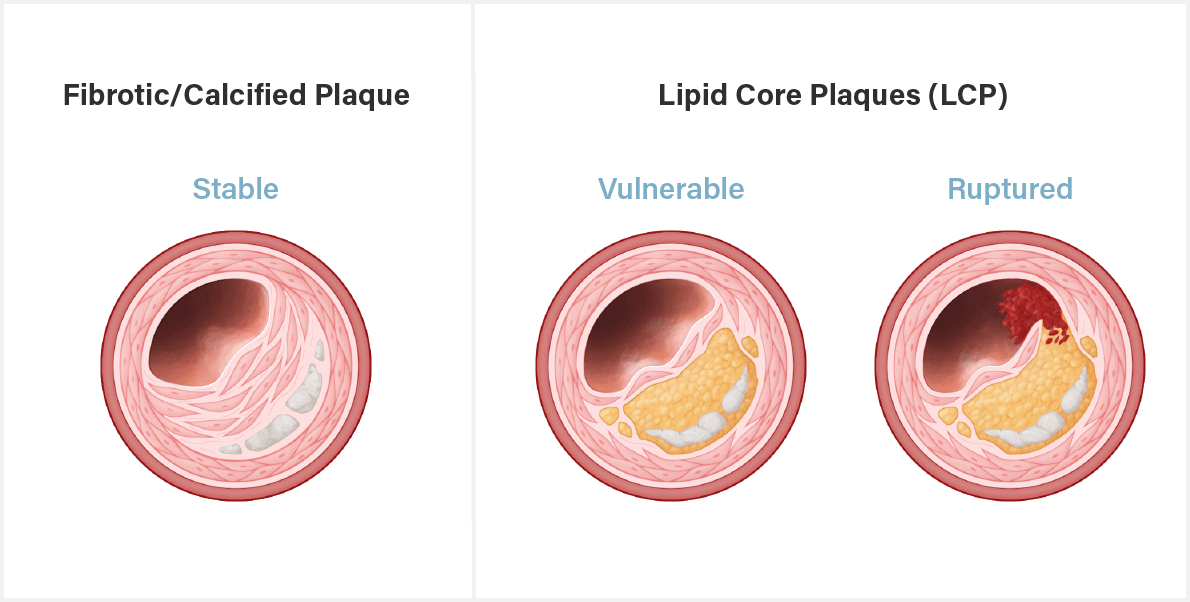

Distinguishing between plaques of different composition is crucial for accurately predicting and managing a patient’s risk of new or recurring cardiovascular events. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy, or NIRS, technology can help interventional cardiologists determine not only a plaque’s structure, but its composition as well. The ability to identify dangerous plaques can help clinicians improve the prognosis of high-risk patients.
Discover IVUS+NIRS
Learn More© 2024 Infraredx™, Inc. All Rights Reserved Powered by Bloom Creative